集群健康状态:
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_cat/health?v"
集群节点列表:
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_cat/nodes?v"
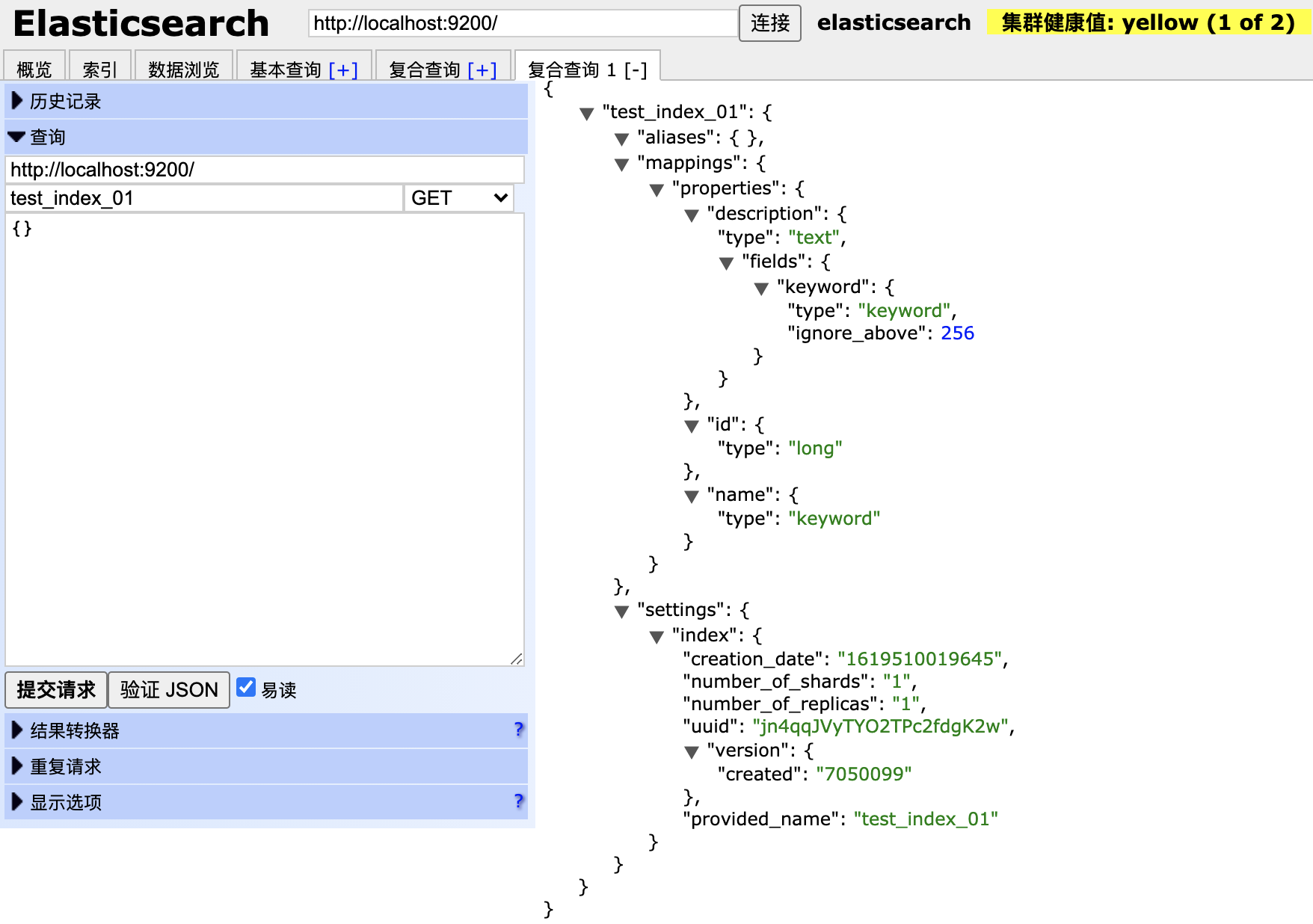
查看所有索引:
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_cat/indices?v"
创建一个customer索引:
curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/customer?pretty"
查看customer索引:
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_cat/indices?v"
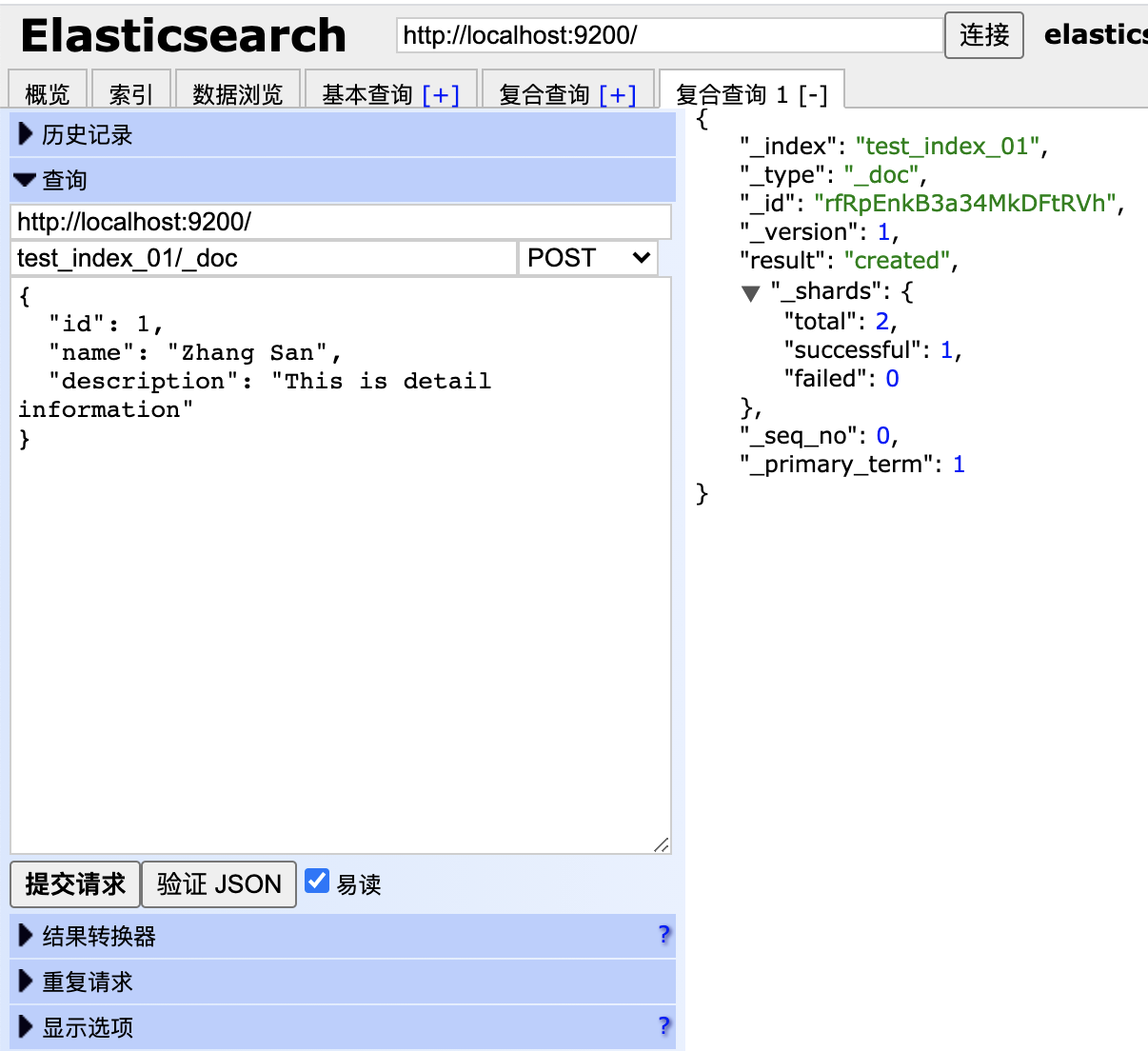
Put一些数据到我们的"customer"索引:
curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/customer/_doc/1?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'{"name": "John Doe"}'
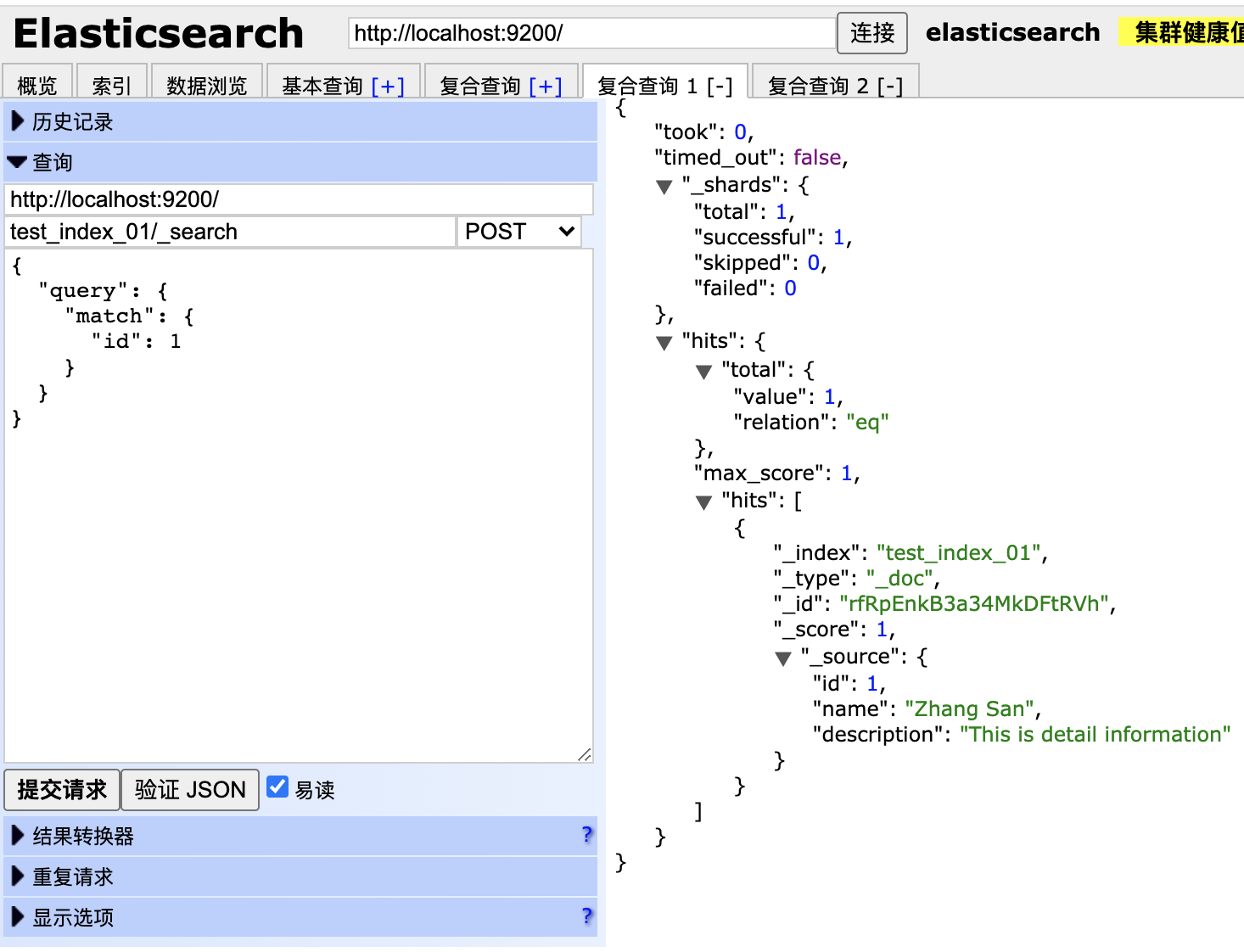
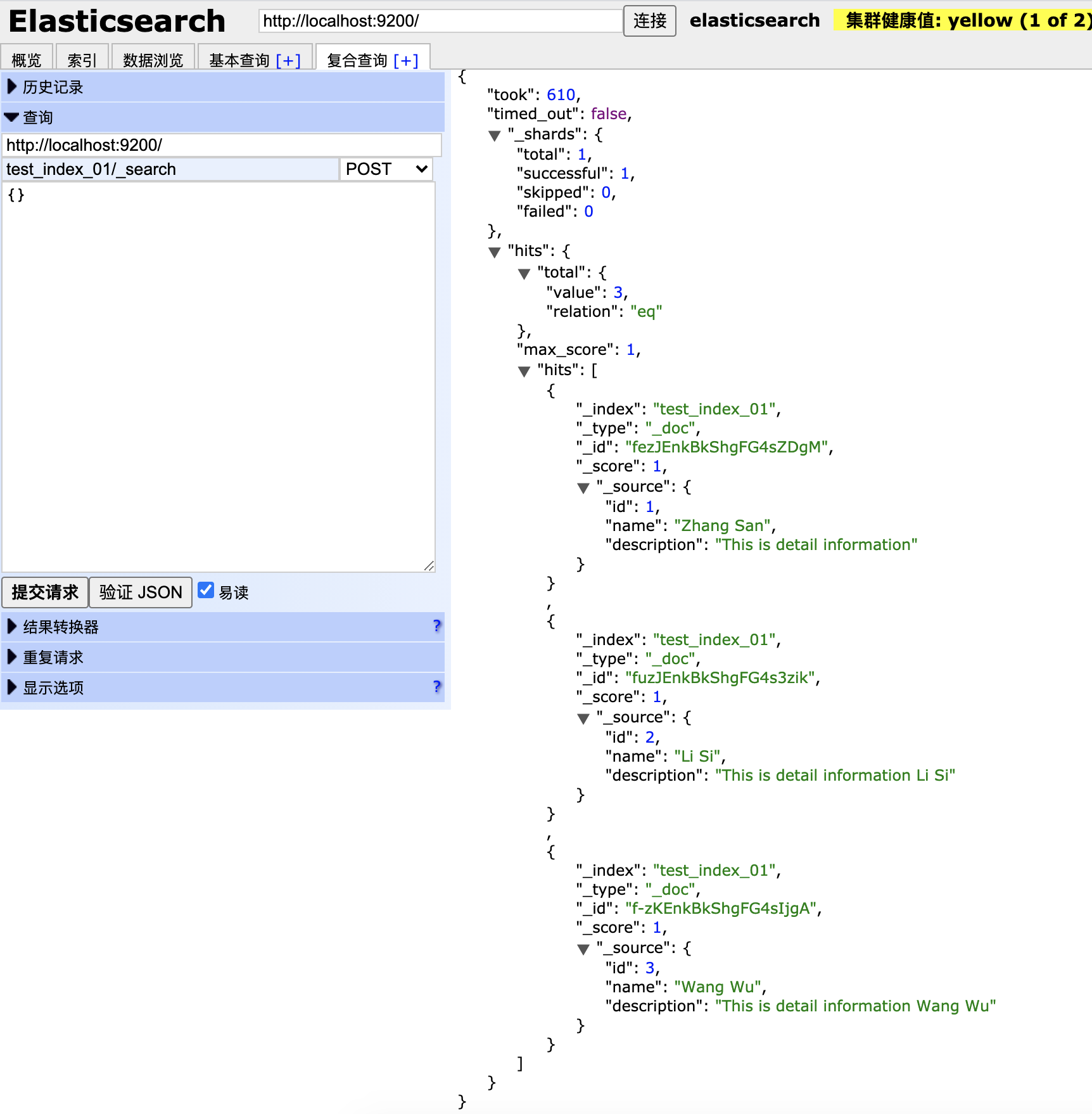
检索这个索引:
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/customer/_doc/1?pretty"
删除索引:
curl -X DELETE "localhost:9200/customer?pretty"
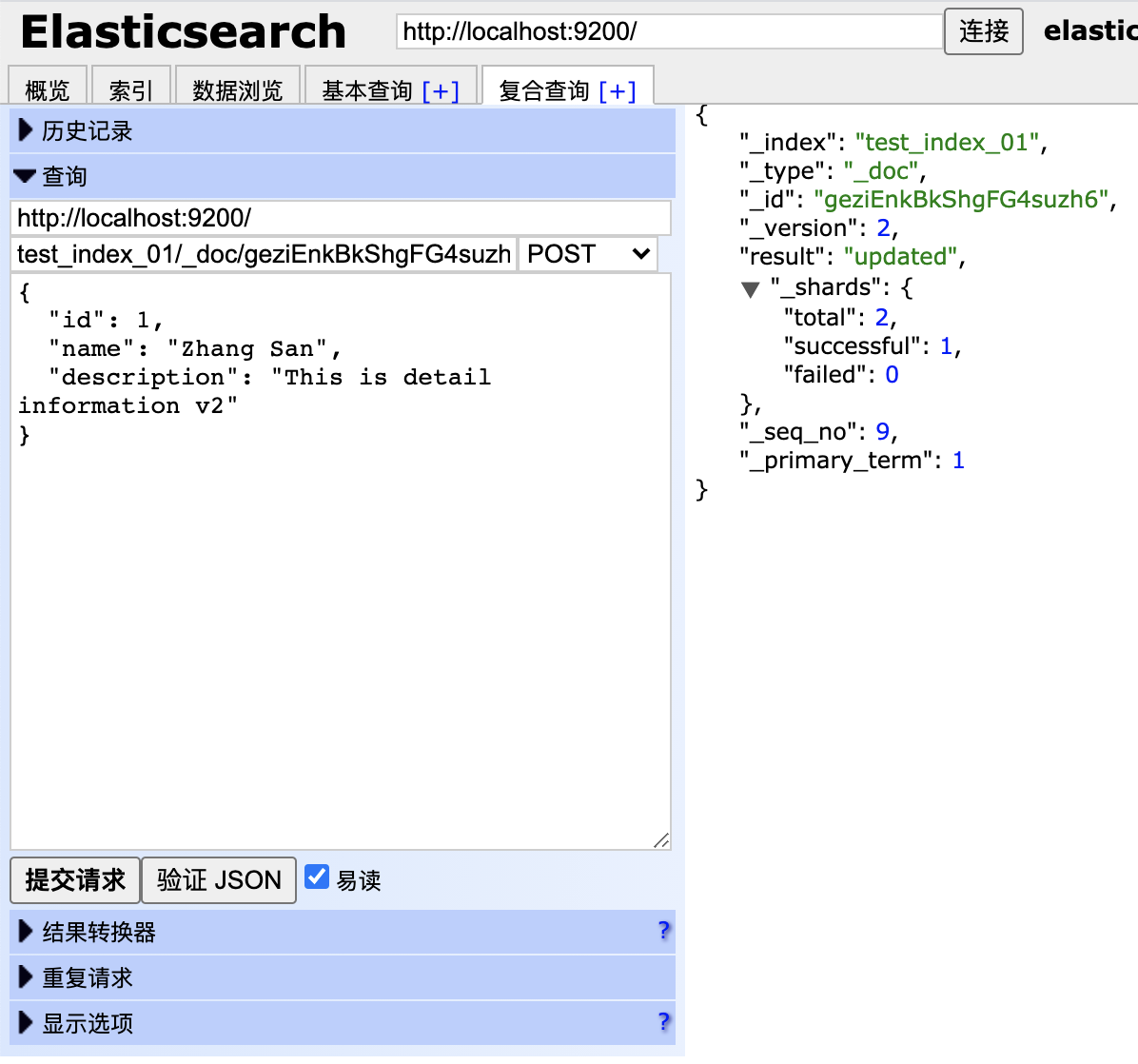
更新索引:
curl -X POST "localhost:9200/customer/_doc/1/_update?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' { "doc": { "name": "Jane Doe", "age": 20 } } '
curl -X POST "localhost:9200/customer/_doc/1/_update?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' { "script" : "ctx._source.age += 5" } '
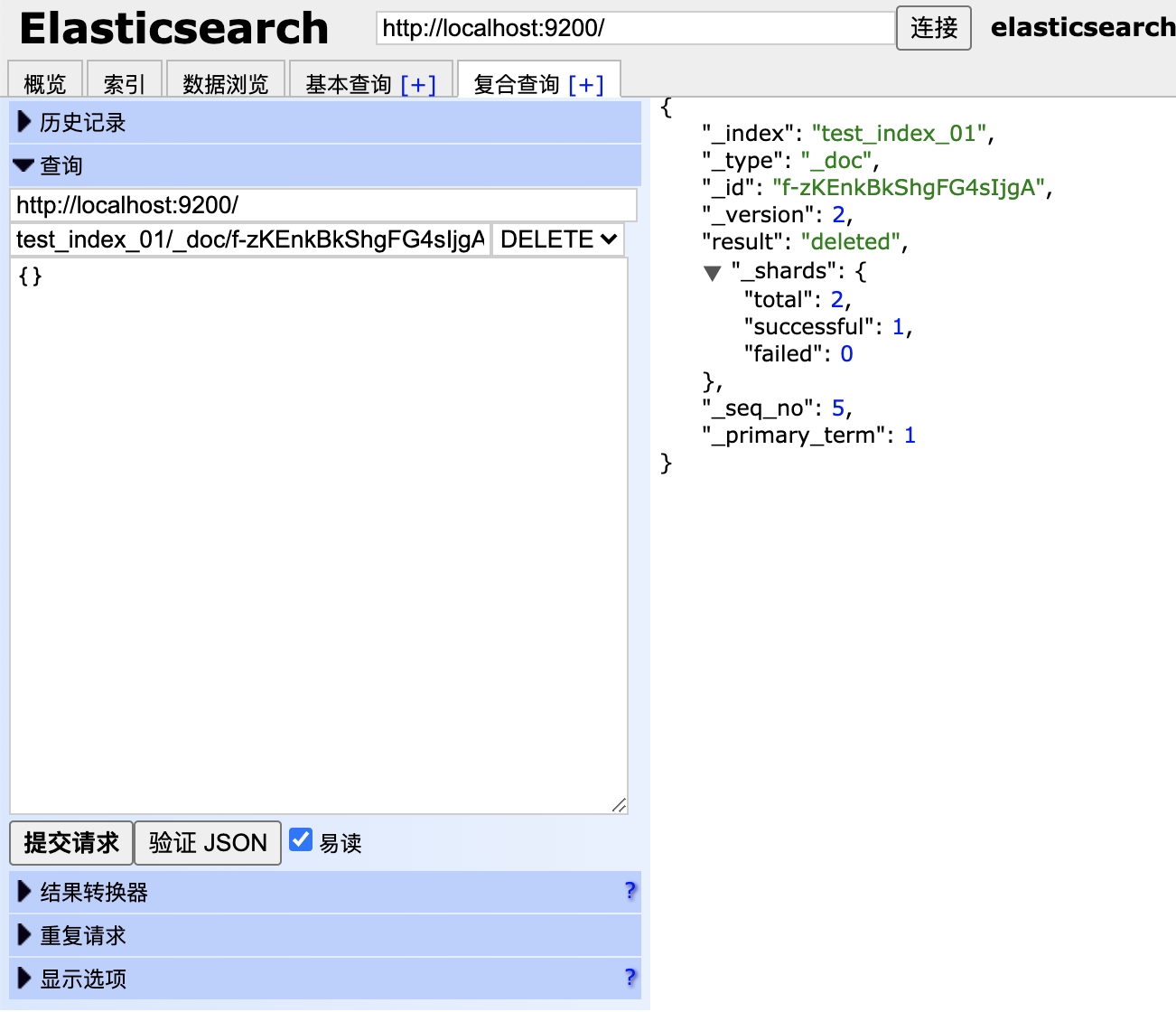
删除文档:
curl -X DELETE "localhost:9200/customer/_doc/2?pretty"